
There is a tendency to point the finger towards the cavity as on the first incident, the patient felt pressure in his chest and on the second incident he reported retrosternal chest pain, which increased, on inspiration and this would be more possible with air in the chest cavity more than a case of PFO.Ĭavitating lung lesions are not an uncommon report in tropical and subtropical countries in Egypt, we see cases of tuberculous and amoebic lung abscesses, which would be no surprise as Entamoeba Histolytica infection is common in touristic areas and other areas as Egyptian delta. It is logical that the two post dive incidents are related to an embolic lesion, and it could have been that the cavity was there at the time of first incident. ConclusionĪnalysing this case with presentation of a severe neurological injury of the central nervous system following gas embolism, one is left in confusion whether the PFO or the lung cavity or both should be blamed. Further treatment was continued at his home country after his departure. The patient showed slow progressive in-complete recovery and was left with residual weakness in the legs and foot, he was able to walk with crutches, with faint reduction in sensory perception over the dorsum of feet bilaterally, sphincter control was regained. Neurologically, patient was drowsy and irritable, reduced sensation from mammary line to feet and severe para paresis, more pronounced on right lower limb, absent superficial abdominal reflexes, knee and ankle hyper-reflexia, positive Babinksi's, positive clonus, stool and urine retention. The patient reported retrosternal chest pain and there was audible reduced air entry on the lungs associated by generalized coarse crepitations. Examination at our facilityĬlinical findings were as follows: Blood pressure 140/90 mmHg, pulse 114/min, SpO2 93% room air, RR 22/min, pale. The dive performed was non-eventful without any clear precipitating factor, no difficulty in equalization, coughing or straining, no fast ascents or strong currents, and the safety stop was correctly executed.
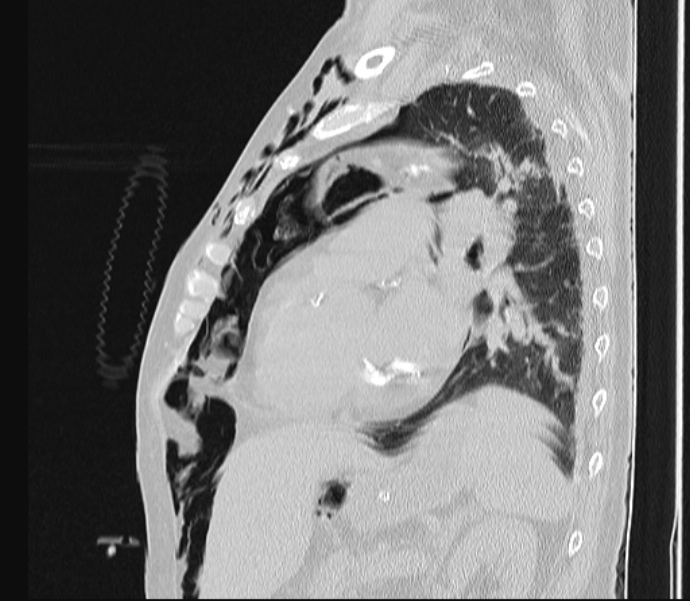
He was brought to HMC (Hyperbaric Medical Center Sharm el Sheikh) by Search and Rescue on oxygen. Shortly after a single 27.4 msw dive for 45 minutes using compressed air in the Red Sea, he suffered acute paraparesis and disturbed conscious level. HistoryĪ 33 year-old male diving instructor with experience (> 600 dives) presented to our facility in 2013. We chose a case for this article with a non-classic history and two concomitant conditions that may precipitate gas embolism to demonstrate the clinical difficulties in diagnosing PBT. It is also worth noting that PBT is a different disorder and is caused by a different mechanism than pulmonary oedema, which is caused by immersion or exhaustion (swimmers lung oedema), where body fluids permeate into the alveolar space and impede gas exchange through the alveolar wall precipitating dyspnea, blood tinged expectoration and respiratory distress.
/GettyImages-155148836-5724c69a3df78ced1f7cc43f.jpg)
Our centre also received cases of PBT caused by heavily straining under water while working on a mooring line or retrieving heavy objects. PBT of ascent occurs among recreational divers who have pre-existing lung diseases whether obstructive, neoplastic, granulomatous or congenital.
Barotrauma lungs free#
There are reports of PBT of ascent occurring in free or buoyant ascents as in submarine escape training which is not a common practice in recreational diving. Hence, conditions or diseases that impede flow of air leaving the lung or causing air trapping may pose a serious health hazard to a scuba diver, spontaneous pneumothorax cases, active asthmatics, cavitating lesions and emphysema, and COPD cases. Gas embolism occurs when air leaks into the blood vessels. If air leaks under the skin, it will cause surgical emphysema.

Leakage of air into the chest cavity will cause a pneumothorax, if it leaks into the pericardium, a pneumo-pericardium or mediastinal emphysema can occur. Leakage of the air from the lungs can present in different ways, depending on the anatomical location.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
